- Introduction
- Importance of Understanding the Digestive System
- Brief Overview of the Digestive Process
- What is the Digestive System?
- Definition and Components
- Primary Functions
- The Journey Begins: The Mouth
- Role of Saliva
- Chewing and Breaking Down Food
- The Esophagus: Food’s Highway
- Function of the Esophagus
- Peristalsis: The Wave-Like Motion
- The Stomach: The Mixing Bowl
- Gastric Juices and Their Role
- Churning and Mixing Process
- Small Intestine: The Absorption Powerhouse
- Structure of the Small Intestine
- Role of Villi and Microvilli
- Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas: The Digestive Helpers
- Functions of the Liver in Digestion
- Role of Bile from the Gallbladder
- Pancreatic Enzymes and Their Importance
- Large Intestine: The Water Recycler
- Absorption of Water and Electrolytes
- Formation and Excretion of Feces
- The Rectum and Anus: The Final Stage
- Storage of Waste
- The Process of Defecation
- Digestive Enzymes: The Chemical Breakdown
- Types of Digestive Enzymes
- How Enzymes Aid in Digestion
- The Role of Gut Microbiota
- What is Gut Microbiota?
- Benefits of a Healthy Gut Flora
- Common Digestive Problems and Solutions
- Acid Reflux and Heartburn
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
- The Impact of Diet on Digestion
- Foods That Promote Healthy Digestion
- Foods to Avoid
- Hydration and Digestion
- Importance of Water
- How Hydration Affects Digestive Health
- Conclusion
- Recap of Key Points
- Final Thoughts on Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System
- FAQs
- How long does it take for food to be digested?
- Can stress affect digestion?
- What are the signs of a healthy digestive system?
- How can I improve my digestion naturally?
- Is it normal to have digestive issues occasionally?
How Our Digestive System Works: A Comprehensive Guide
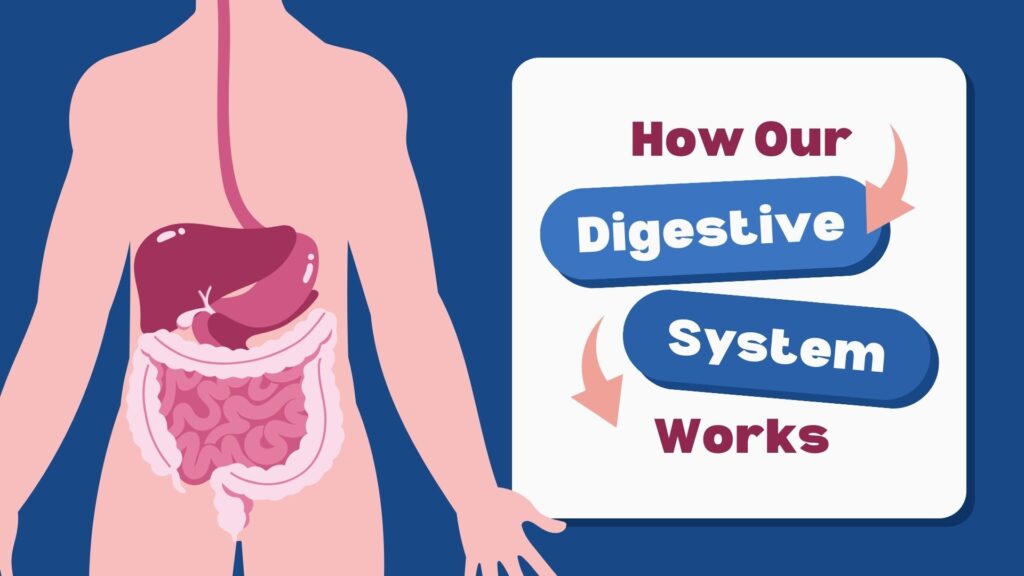
Table of Contents – Digestive System
Introduction
Understanding how our digestive system works is crucial for maintaining overall health. Imagine your body as a complex machine, and the digestive system as its engine. Without proper digestion, our bodies wouldn’t get the necessary nutrients and energy to function. Let’s dive into the fascinating journey of how our digestive system works.
What is the Digestive System?
The digestive system is a series of organs that work together to break down food, absorb nutrients, and expel waste. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. Each part has a specific role, ensuring that our bodies get the nutrients they need to thrive.
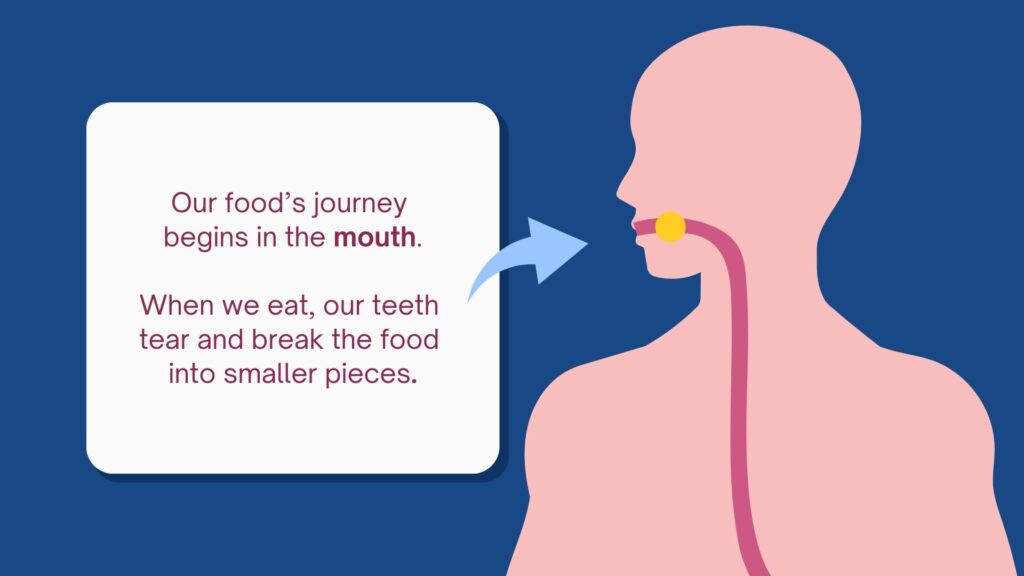
The Journey Begins: The Mouth
Digestion starts in the mouth. Here, food is chewed into smaller pieces by our teeth, a process called mastication. Saliva, produced by the salivary glands, mixes with the food to begin breaking it down chemically. Saliva contains enzymes like amylase that start the digestion of carbohydrates right in the mouth.
The Esophagus: Food’s Highway

Once food is chewed and mixed with saliva, it forms a bolus, which is then swallowed. The esophagus, a muscular tube, serves as the highway for food to travel from the mouth to the stomach. This movement is facilitated by peristalsis, a series of wave-like muscle contractions that push the food downward.
The Stomach: The Mixing Bowl
The stomach is where the real action begins. It acts like a mixing bowl, churning food and mixing it with gastric juices. These juices, which contain hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes, break down proteins and kill bacteria. The stomach muscles churn the food into a semi-liquid form called chyme.
Small Intestine: The Absorption Powerhouse
The small intestine is a long, coiled tube where most of the digestion and absorption of nutrients occur. It has three parts: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The walls of the small intestine are lined with tiny finger-like projections called villi and microvilli, which increase the surface area for absorption. Here, enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver continue the digestion process.
Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas: The Digestive Helpers
The liver, gallbladder, and pancreas play crucial supporting roles in digestion. The liver produces bile, which is stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine to help digest fats. The pancreas produces a range of enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. These enzymes are delivered to the small intestine, where they complete the digestion of food.
Large Intestine: The Water Recycler
After the small intestine has absorbed nutrients, the remaining waste moves into the large intestine. The large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes from the waste material, transforming it into a more solid form called feces. This process is crucial for maintaining the body’s fluid balance.
The Rectum and Anus: The Final Stage
The rectum stores feces until it is ready to be excreted. When the body is ready to eliminate waste, the rectal walls signal the need for a bowel movement. The feces are then expelled through the anus, completing the digestive process.
Digestive Enzymes: The Chemical Breakdown
Digestive enzymes are specialized proteins that speed up the chemical reactions involved in breaking down food. There are several types of digestive enzymes, including:
- Amylase: Breaks down carbohydrates.
- Protease: Breaks down proteins.
- Lipase: Breaks down fats.
These enzymes are essential for converting complex food molecules into simple nutrients that the body can absorb.
The Role of Gut Microbiota
The gut microbiota consists of trillions of microorganisms living in our intestines. These microbes play a vital role in digestion, helping to break down complex carbohydrates and fiber that our bodies can’t digest on their own. A healthy gut flora supports the immune system, synthesizes vitamins, and prevents the growth of harmful bacteria.
Common Digestive Problems and Solutions
Digestive issues can affect anyone. Common problems include:
- Acid Reflux and Heartburn: Caused by stomach acid rising into the esophagus.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A chronic condition characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
Solutions often involve lifestyle changes such as eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods, staying hydrated, and managing stress.
The Impact of Diet on Digestion
What we eat significantly impacts our digestion. Foods that promote healthy digestion include:
- Fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Fermented foods like yogurt and kefir, which contain probiotics.
- Lean proteins and healthy fats.
Conversely, foods high in sugar, fat, and processed ingredients can hinder digestion and cause problems like bloating and constipation.
Hydration and Digestion

Staying hydrated is vital for good digestion. Water helps dissolve nutrients and move them through the digestive tract. It also softens stool, preventing constipation. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your digestive system running smoothly.
Conclusion
Understanding the digestive system is key to maintaining overall health. By knowing how each part of the system works, from the mouth to the anus, and how diet and lifestyle choices impact digestion, we can take steps to support our digestive health. Remember to eat a balanced diet, stay hydrated, and manage stress to keep your digestive system in top shape.
FAQs
How long does it take for food to be digested? Typically, it takes about 6 to 8 hours for food to pass through the stomach and small intestine. The complete process, including the large intestine, can take up to 24 to 72 hours.
Can stress affect digestion? Yes, stress can significantly impact digestion, causing issues like acid reflux, IBS, and changes in bowel habits. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can help improve digestive health.
What are the signs of a healthy digestive system? A healthy digestive system typically shows regular bowel movements, no pain or discomfort, and the ability to digest food without issues like bloating or gas.
How can I improve my digestion naturally? You can improve digestion by eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and managing stress. Probiotics and fermented foods can also support gut health.
Is it normal to have digestive issues occasionally? Yes, occasional digestive issues are normal and often related to diet or stress. However, persistent problems should be addressed with a healthcare professional.
The Impact of Physical Activity on Digestion
Physical activity is not only good for overall health but also plays a vital role in promoting efficient digestion. Exercise helps stimulate the natural contraction of intestinal muscles, which helps move food through the digestive system more efficiently. Regular physical activity can prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements.
Types of Exercises Beneficial for Digestion:
- Walking: A simple yet effective way to stimulate digestion. A short walk after meals can help speed up the digestive process.
- Yoga: Certain yoga poses, such as twists and forward bends, can massage the digestive organs and promote better function.
- Core Strengthening Exercises: Activities that strengthen the abdominal muscles can support the digestive organs and improve overall digestion.
The Role of Sleep in Digestive Health
Adequate sleep is essential for the body to perform its vital functions, including digestion. Poor sleep can disrupt the balance of gut microbiota and lead to digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Tips for Better Sleep to Aid Digestion:
- Establish a Regular Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day can improve sleep quality.
- Avoid Heavy Meals Before Bed: Eating large or spicy meals close to bedtime can cause discomfort and disrupt sleep.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Activities such as reading, listening to soothing music, or taking a warm bath can help signal to your body that it’s time to wind down.
The Importance of Mindful Eating
Mindful eating is a practice that involves paying full attention to the eating experience without distractions. This approach can improve digestion by allowing the body to properly process and absorb nutrients.
How to Practice Mindful Eating:
- Eat Slowly: Take time to chew food thoroughly, which aids in breaking down food and makes it easier for the stomach to digest.
- Focus on the Meal: Avoid distractions such as TV or smartphones during meals. Concentrate on the taste, texture, and aroma of the food.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues. Stop eating when you feel satisfied, not stuffed.
Understanding Food Intolerances and Allergies
Food intolerances and allergies can significantly impact digestion. It’s important to recognize the symptoms and understand how to manage these conditions.
Common Food Intolerances:
- Lactose Intolerance: The inability to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products, can cause bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
- Gluten Sensitivity: Non-celiac gluten sensitivity can cause digestive symptoms such as bloating and abdominal pain after consuming gluten-containing foods.
Managing Food Allergies:
- Read Labels Carefully: Always check food labels for potential allergens.
- Avoid Cross-Contamination: Use separate utensils and preparation areas to avoid cross-contact with allergens.
- Seek Professional Help: Consult a healthcare provider or nutritionist for personalized advice and management strategies.
The Benefits of Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics and prebiotics play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that help balance the gut microbiota, while prebiotics are types of fiber that feed these good bacteria.
Sources of Probiotics:
- Yogurt: Contains live and active cultures.
- Kefir: A fermented milk drink rich in probiotics.
- Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage that provides a good source of probiotics.
Sources of Prebiotics:
- Garlic: Contains inulin, a type of prebiotic fiber.
- Onions: High in prebiotic fibers.
- Bananas: A convenient source of prebiotics that also provides other essential nutrients.
The Connection Between Mental Health and Digestion
The brain and digestive system are closely connected, often referred to as the gut-brain axis. Mental health can have a direct impact on digestion and vice versa.
How Mental Health Affects Digestion:
- Stress: Chronic stress can alter gut motility and increase the risk of digestive disorders.
- Anxiety and Depression: These conditions can lead to changes in appetite and digestion, resulting in symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, or constipation.
Improving Mental Health for Better Digestion:
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Activities such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can reduce stress levels.
- Seek Support: Talking to a therapist or joining a support group can help manage mental health conditions.
- Maintain a Balanced Lifestyle: Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and sufficient sleep are essential for both mental and digestive health.
Conclusion
Understanding how our digestive system works is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. By recognizing the roles of different organs, the importance of diet, hydration, physical activity, sleep, and mental health, we can take proactive steps to support our digestive health. Remember, a healthy digestive system is the foundation of a healthy body. Make mindful choices, stay informed, and prioritize your digestive wellness.
FAQs
How long does it take for food to be digested? Typically, it takes about 6 to 8 hours for food to pass through the stomach and small intestine. The complete process, including the large intestine, can take up to 24 to 72 hours.
Can stress affect digestion? Yes, stress can significantly impact digestion, causing issues like acid reflux, IBS, and changes in bowel habits. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can help improve digestive health.
What are the signs of a healthy digestive system? A healthy digestive system typically shows regular bowel movements, no pain or discomfort, and the ability to digest food without issues like bloating or gas.
How can I improve my digestion naturally? You can improve digestion by eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and managing stress. Probiotics and fermented foods can also support gut health.
Is it normal to have digestive issues occasionally? Yes, occasional digestive issues are normal and often related to diet or stress. However, persistent problems should be addressed with a healthcare professional.
The Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Digestive Health
Lifestyle choices play a significant role in how efficiently our digestive system functions. From what we eat to how we handle stress, these factors can either support or hinder our digestive health.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits for Better Digestion:
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods helps ensure that your digestive system has all the resources it needs to function correctly.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps keep food moving through your digestive system and reduces the risk of constipation.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough rest is crucial for allowing your body, including your digestive system, to repair and rejuvenate.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness
meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can significantly reduce stress levels, which in turn can improve digestive health.
The Role of Fiber in Digestion
Fiber is a crucial component of a healthy diet, particularly for digestion. It comes in two forms: soluble and insoluble, both of which play essential roles.
Soluble Fiber:
- Function: Dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance, which helps lower blood cholesterol and glucose levels.
- Sources: Oats, peas, beans, apples, citrus fruits, carrots, barley.
Insoluble Fiber:
- Function: Adds bulk to the stool and helps food pass more quickly through the stomach and intestines.
- Sources: Whole-wheat flour, wheat bran, nuts, beans, and vegetables like cauliflower and potatoes.
Benefits of Fiber:
- Prevents Constipation: By adding bulk and softening the stool.
- Maintains Bowel Health: Helps to normalize bowel movements and prevent digestive disorders like diverticulitis.
- Aids in Weight Management: High-fiber foods are more filling, which can help control appetite and reduce overall calorie intake.
Digestive System Disorders: Symptoms and Prevention
Understanding the common symptoms of digestive disorders can help in early detection and treatment. Here are some typical disorders and their preventive measures.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
- Symptoms: Heartburn, regurgitation, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing.
- Prevention: Avoid trigger foods (spicy, fatty, and acidic foods), eat smaller meals, and avoid lying down immediately after eating.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
- Symptoms: Abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation.
- Prevention: Maintain a high-fiber diet, stay hydrated, and manage stress.
Lactose Intolerance:
- Symptoms: Bloating, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps after consuming dairy products.
- Prevention: Limit or avoid lactose-containing foods, use lactose-free products or take lactase supplements.
Celiac Disease:
- Symptoms: Diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, bloating, and anemia.
- Prevention: Adhere to a strict gluten-free diet.
Natural Remedies for Digestive Health
In addition to medical treatments, several natural remedies can support digestive health and alleviate common symptoms.
Herbal Teas:
- Ginger Tea: Helps reduce nausea and improve digestion.
- Peppermint Tea: Soothes the digestive tract and relieves symptoms of IBS.
- Chamomile Tea: Reduces inflammation and helps with stomach cramps.
Probiotic Supplements:
- Function: Enhance the gut microbiota, improve digestion, and boost the immune system.
- Sources: Available in capsules, powders, and as part of fermented foods like yogurt and kefir.
Apple Cider Vinegar:
- Function: Improves digestion and balances stomach acid levels.
- Usage: Mix a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar in a glass of water and drink before meals.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System
Maintaining digestive health requires a holistic approach, considering diet, lifestyle, and mental well-being.
Dietary Tips:
- Eat Regular Meals: Regular eating patterns help regulate digestive activity.
- Chew Food Thoroughly: This makes it easier for your stomach to break down the food.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Lifestyle Tips:
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your daily routine.
Mental Well-being:
- Practice Mindfulness: Techniques like meditation can reduce stress and improve gut health.
- Stay Connected: Social interactions and emotional support are crucial for mental and digestive health.
Conclusion
Understanding how our digestive system works and what it needs to function optimally is essential for maintaining overall health. From the initial breakdown of food in the mouth to the absorption of nutrients in the intestines, every step of the digestive process is crucial. By making informed choices about diet, exercise, hydration, and stress management, we can support our digestive system and enhance our overall well-being. Remember, a healthy gut contributes to a healthy life, so take care of your digestive health with the attention it deserves.
FAQs
How long does it take for food to be digested? Typically, it takes about 6 to 8 hours for food to pass through the stomach and small intestine. The complete process, including the large intestine, can take up to 24 to 72 hours.
Can stress affect digestion? Yes, stress can significantly impact digestion, causing issues like acid reflux, IBS, and changes in bowel habits. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can help improve digestive health.
What are the signs of a healthy digestive system? A healthy digestive system typically shows regular bowel movements, no pain or discomfort, and the ability to digest food without issues like bloating or gas.
How can I improve my digestion naturally? You can improve digestion by eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and managing stress. Probiotics and fermented foods can also support gut health.
Is it normal to have digestive issues occasionally? Yes, occasional digestive issues are normal and often related to diet or stress. However, persistent problems should be addressed with a healthcare professional.




















